What Is Biodiversity and Why It Matters?
TLDR
Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth, from genes to species to whole ecosystems. We rely on it every day for clean air and water and food. Kelp forests are a great example of biodiversity in action. When biodiversity is lost, ecosystems become less resilient and the services people depend on start to break down.
Why talk about biodiversity now?
Biodiversity is more than a buzzword
“Biodiversity” gets thrown around a lot. The truth is, biodiversity is critically important, and whether you understand it or not, you absolutely depend on it for clean air, fresh water, food, and stable environments. Instead of treating it as a buzzword, this article slows down and looks at what biodiversity means, then zooms in on kelp forests as a living example.
What is biodiversity?
A simple definition
Put simply, Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth, encompassing the diversity of species, genes, and ecosystems. It’s also a key indicator of the health and stability of an ecosystem.
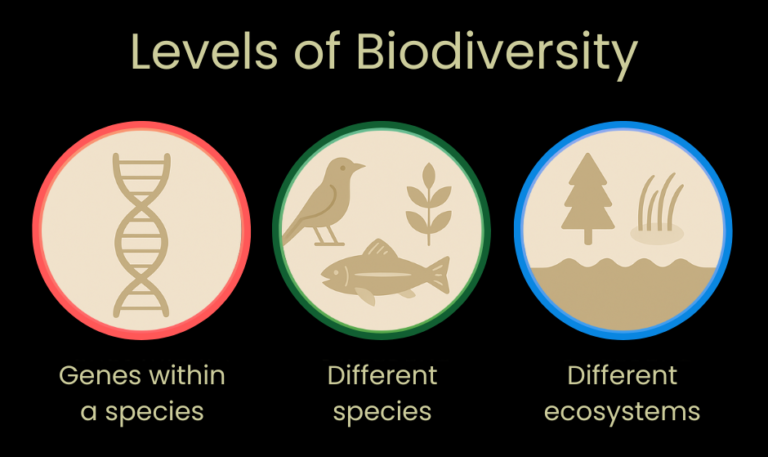
Three levels of biodiversity
You can think of biodiversity in three connected layers:
- Species diversity: the different species of plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms in an area, for example the mix of trees, birds, and insects in a forest.
- Genetic diversity: the variety of genes within those species, such as different strains of the same crop species that help farmers cope with pests, disease, or drought.
- Ecosystem diversity: the diversity of ecosystems and the interactions between organisms and their environments, for example forests, wetlands, and coastal kelp forests within a region.
Taken together, these layers shape how biodiversity functions in nature. When there are more kinds of species, genes, and habitats sharing the workload, ecosystems are better able to keep providing clean air and water, fertile soil, and more stable climates.
Why biodiversity matters in kelp forests?
Kelp forests as foundation ecosystems
In kelp forests, biodiversity is high and performs critical functions that support many marine species and provide vital services to humans. Certain species of kelp act as foundation species, creating three-dimensional underwater forests that the wider ecosystem relies on to function.
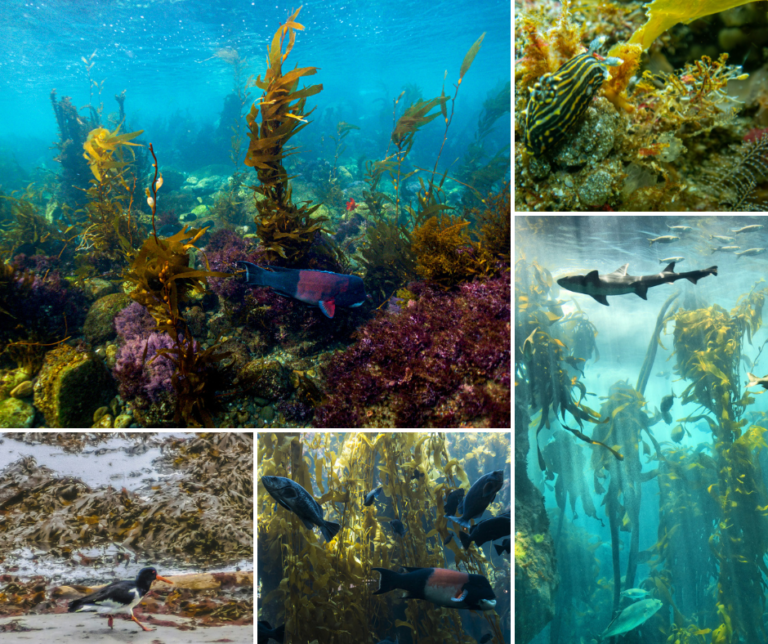

How biodiversity keeps kelp forests resilient
Kelp forest biodiversity operates on multiple levels:
- Ecosystem diversity: different kelp species, for example canopy-forming giants and shorter understory species, add structural complexity and create microhabitats that allow many species to coexist.
- Species diversity: these underwater forests provide food, shelter, and protection for fish, crabs, octopuses, sea otters, seals, and countless other critters.
- Genetic diversity: within a single kelp species, high genetic variation is crucial for the population’s ability to adapt to environmental stressors like marine heatwaves or disease. Research has shown that low-diversity kelp populations were more vulnerable to collapse during extreme climate events, while high-diversity populations were more resilient.
A classic example of biodiversity in action is the relationship between sea otters, sea urchins, and kelp. Sea otters are a keystone species that prey on sea urchins. Without otters to control the urchin population, urchins can overgraze the kelp, turning a biodiverse forest into a sparse “urchin barren”.
Where restoration fits in
Restoring kelp forests to protect biodiversity
Restoring kelp forests is one practical way to support biodiversity and resilience. By rebuilding kelp habitat, restoration projects can help re-establish structural habitat, support species diversity, and maintain or enhance genetic diversity within kelp populations.
At West Coast Kelp, biodiversity is not just a scientific term. It is one of the main reasons we focus on restoring kelp forests in the first place, and it guides where we work, how we design projects, and how we measure whether those projects are actually rebuilding resilient marine ecosystems.
Watch biodiversity in action in kelp forests
Biodiversity makes ecosystems that humans rely on more resilient, and kelp forests are a great example of how that plays out in the real world.
